The 2021 MDSGC Student Research Symposium was held via Zoom on Wednesday, August 4, beginning at 9 a.m. EDT.
This year’s symposium showcased presentations by student interns and researchers working at sites across Maryland. The cohort of presenters represented diverse institutions, including: Capitol Technology University, Hagerstown Community College, Morgan State University, NASA Wallops and NASA Ames, Towson University, University of Maryland Baltimore County, University of Maryland College Park, University of Maryland Eastern Shore, and West Virginia University. We congratulate our students on a successful summer, under trying circumstances, and look forward to seeing more of their work in the future!
The full program follows.
2021 MDSGC (Virtual) Student Research Symposium Program
Session 1
The earth is cooled through a process known as radiative cooling. Radiative cooling is seen in many substances and allows a substrate to cool itself below ambient temperatures. Finding substances that use radiative cooling will allow us to cool surfaces without the use of energy.
This presentation highlights the various activities done to understand science applications in space. It also follows the journey to create a homemade piston launch system that can operate pneumatically and hydraulically.
Throughout this 10-week internship, I was tasked with researching space related physics topics such as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, rotational motion, and gyroscopic motion to make a module that could help educate others about how they impact engineering design in space. I began by looking into rockets, but specifically rocket stability, and how the balancing of the aerodynamic forces is essential for the rocket to achieve stable flight. This involved extensive research into the effect of both the center of gravity (CG) and the center of pressure (CP), and their location along the body of a rocket. I ended up developing a one-page module that allows the STEM center to teach students and educators how to approximate the CP on a rocket and verify that it would be able to achieve stable flight before launching it. Ultimately, I was able to teach this module to 60+ teachers at the SET Sail event in July and provide them with a better understanding about engineering design and rocket stability.
Since finishing the rocket module in mid-July, I have moved on to magnetism and started to work on creating a maglev that would be used within a 1-hour magnetic principles module. I have not completed it yet, but I still have 2 remaining weeks to complete it, and I have made substantial improvements to its design. Working alongside the tool shop on campus, I submitted engineering drawings and had three versions manufactured out of wood, and I am waiting to test the final version. Although this wood version is incomplete, I have been able to utilize Legos to make a modular maglev model that can be customized to one’s preferences and allows for manipulation of both the train tracks and the car to test different designs. It has been very successful thus far and I plan on using both the wooden and Lego maglev in the development of a module.
This presentation will cover the hardware selection and design process for subassemblies on the Centrifugal Mirror Fusion Experiment (CMFX). The gas puff valve system and capacitor rack redesign will be discussed in detail.
Using kilobots, two emergent behaviors will be put in the same environment to see how they interact with each other. The first emergent behavior is based off potential cell repair with kilobots using gradient to find and surround damaged cells. The second is based off typical herding behavior of animals. The two emergent behaviors have a similar end result using two different parameters. When put in the same environment it seems the behaviors don’t interact as the herding kilo bots form separately from the gradient kilobots who focus only on one kilobot to surround.
The standard line element in general relativity contains 4-dimensions (3 spatial and one temporal). It seems plausible that adding mass as a 5th coordinate will more accurately describe the physical world. This talk will motivate the use of this 5-dimensional line element. A particular form of 5-dimensional metric will also be presented along with some attempts at testing this metric physically.
In physics, there is an idea that multiple universes may exist. One of these possible universes is the cartoon universe. The differences between our universe to that of the Looney Tooniverse will be observed in this presentation. .
We will pause for questions to the first group of presenters. Questions may be entered in Zoom chat or online Q&A tool — be sure to specify to which presenter your question is addressed. If time permits additional questions will be taken from the audience — use “Raise Hand” function to be called on by moderators.
-
-
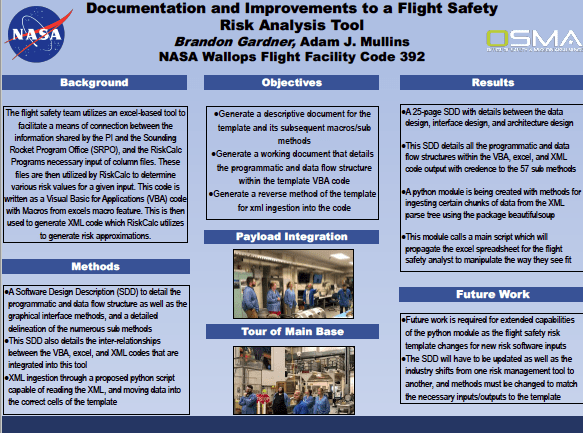
- Documentation and Improvements to a NASA Flight Safety Risk Tool — Mr. Brandon Gardner (UMES / NASA WFF)
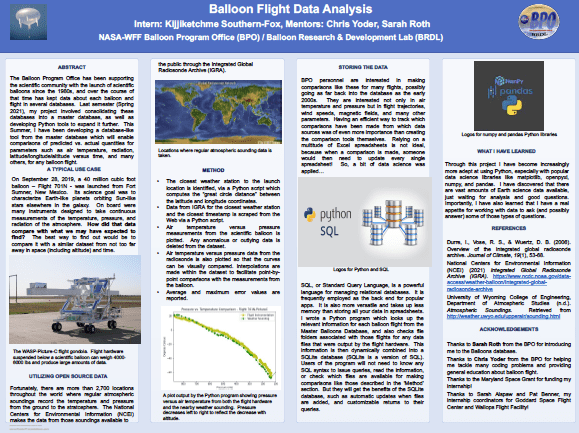
- Balloon Flight Data Analysis — Mr. Kijjiketchme Southern-Fox (UMES / NASA WFF)
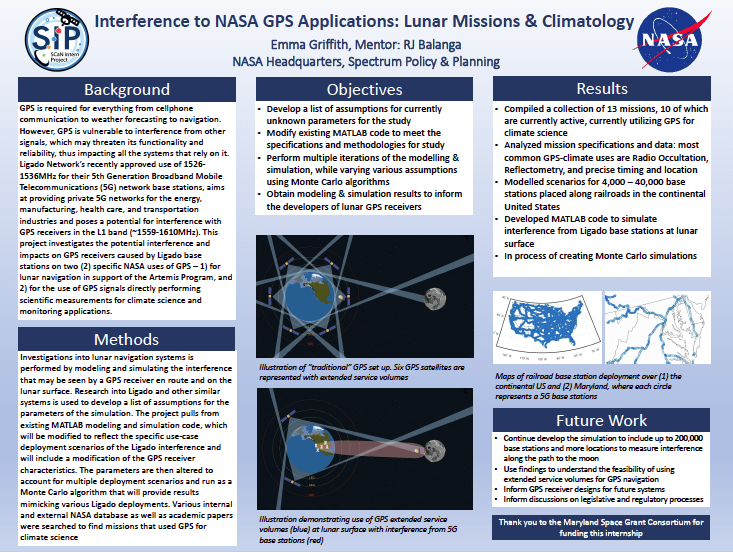
- Interference to NASA GPS Applications: Lunar Missions & Climatology — Ms. Emma Griffith (UMD / NASA HQ)
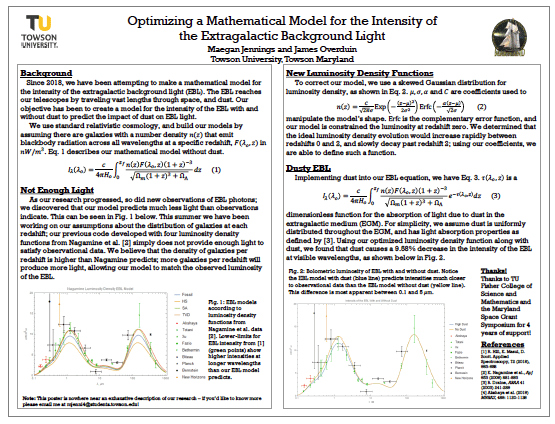
- Optimizing a Mathematical Model for the Intensity of the Extragalactic Background Light — Ms. Maegan Jennings (TU)
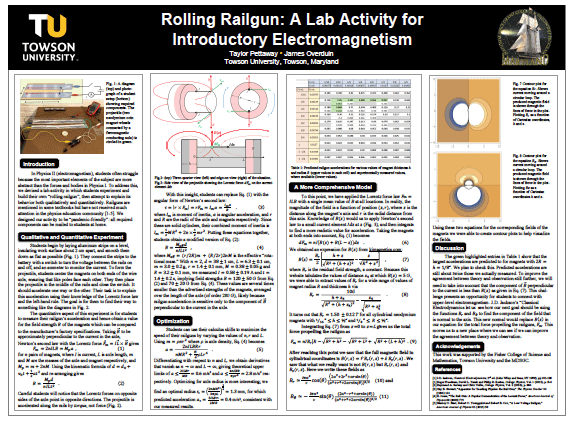
- Rolling Railgun: A Lab Activity for Introductory Electromagnetism — Ms. Taylor Pettaway (TU)
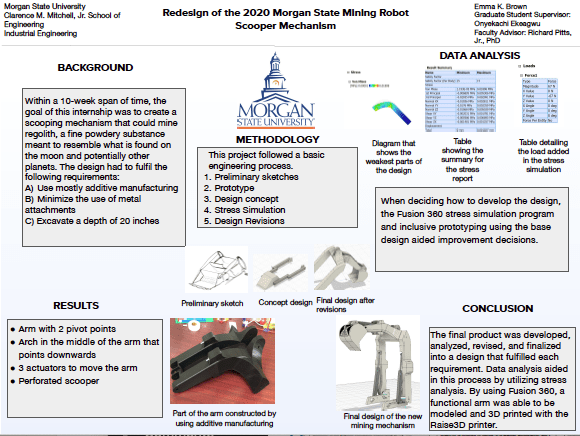
- Redesign of the 2020 Morgan State Mining Robot Scooper Mechanism — Ms. Emma Brown (UMCP / MSU)
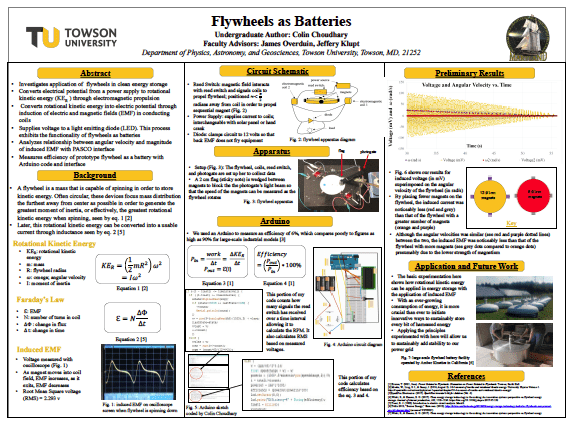
- Flywheels as Batteries — Mr. Colin Choudhary (TU)
-
Feasibility of using Wifi for high-speed communications with High-Altitude Balloons, drones, and other platforms — Mr. Ethan Hart (UMES / CTU)
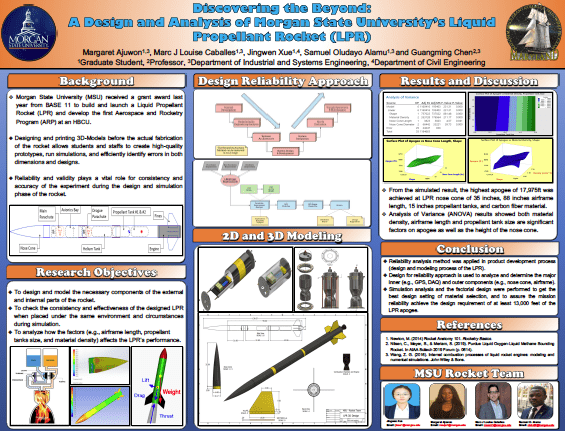
- Discovering the Beyond: Design and Analysis of Morgan State University Liquid Propellant Rocket — Ms. Margaret Ajuwon (MSU)
- Participation in RockOn 2021 Sounding Rocket Program Launch by NASA — Mr. Marc Caballes and Mr. Sam Alamu (MSU)
-
Virtual Poster Session
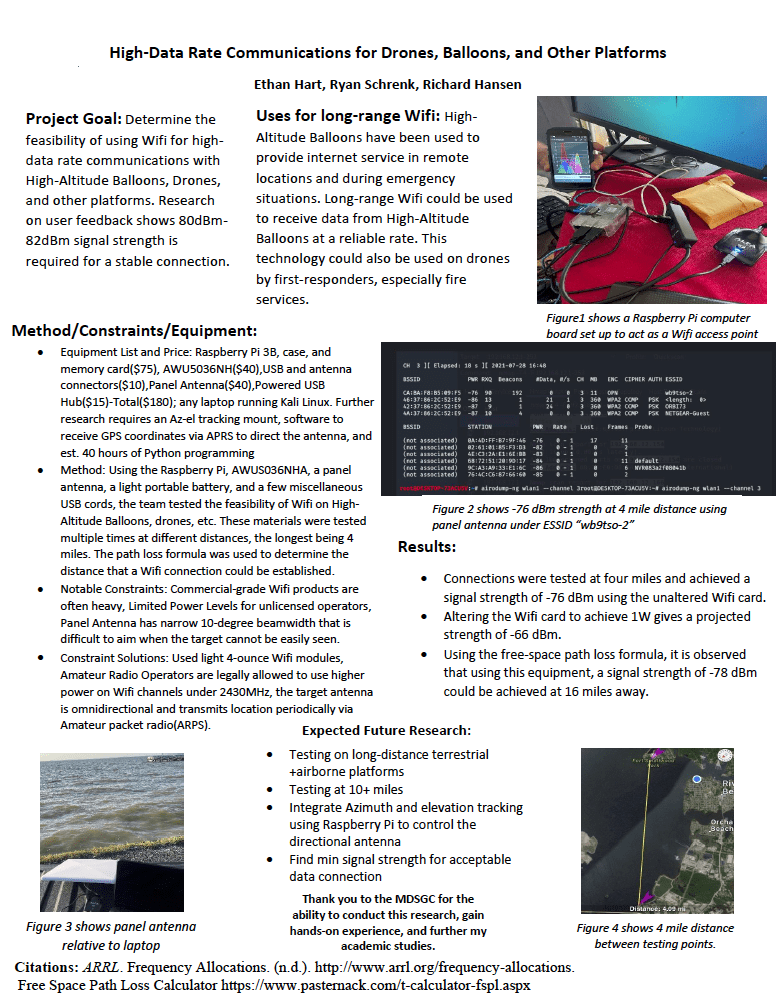
— Mr. Ethan Hart (UMES / CTU)

We will reconvene for questions related to poster presentations and any remaining questions for earlier presenters. Questions may be entered in Zoom chat or online Q&A tool — be sure to specify to which presenter your question is addressed. If time permits additional questions will be taken from the audience — use “Raise Hand” function to be called on by moderators.
Session 2
Sensing, actuation, and control are integral to smart devices with embedded microcontrollers. Arduino and Raspberry Pi microcontrollers and single-board computers can be interfaced with various sensors and actuators and incorporated in mechanical devices to perform a variety of intelligent functions using appropriate software programming. In this presentation use of C++(Sketch), Scratch, Bloxter, and Python programs compiled and executed on Arduino and Raspberry Pi boards interfaced with various sensors and actuators will be elaborated. A novel application using a soft gripper mounted on a mobile robotic device embedded with a Raspberry Pi board will be outlined. Path following application using a light sensor will also be demonstrated on the mobile device using three different methods including proportional, integral, and, derivative (PID) control. The different methods will be compared using path following error data collected and plotted using MATLAB software. With appropriate trials well-tuned PID gains have been identified that ensure accurate path following at different speeds of the mobile robotic platform. A Python program has been developed that allows the user to input any desired speed and the device accurately tracks the path using PID control using interpolated gain values autonomously. The internship also provided an opportunity to get exposure to other activities in the Robotics and Manufacturing Automation Lab at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore(UMES) including industrial robotic arms, soft robotics, and digital agriculture applications using FarmBots, drones, robotic boats, and ground robots.
Air pollution is a global health concern and has led to millions of premature deaths. In overpopulated cities, pollutants such as PM2.5, ozone, and NO2 have disastrous effects on human health and exacerbate respiratory illnesses. COVID-19 related lockdowns and restrictions have played a major role in air quality and human health. The cities observed in this study are Milan, Kolkata, São Paulo, Los Angeles, and Sydney. The biggest contributors to air pollution in Los Angeles and Sydney were natural wildfires that increased concentrations of PM2.5. In Kolkata trash burning, diesel engines, and coal combustion led PM2.5 and NO2 to increase during the winter months. Milan’s topography promoted PM2.5 concentrations by casting a thick and protective fog over the area during the winter months. The deforestation of the rainforests in Brazil promoted PM2.5 by causing droughts in Sao Paulo, which made the city very dusty, and worsened the air quality. By analyzing the effects of the COVID-19 pandemics on air quality, the scope for environmental restoration is seen as people and governments learn what contributes to air quality, and how humans can manipulate it. The findings from this study, and other contemporary ones, could aid in efforts towards combating climate change, and sustaining human life.
The summer internship and exchange program hosted by Maryland Space Grant Consortium (MDSGC) consists of a 10-weeks internship program in the five participating universities in Maryland. The goal of this internship study is to design, build, and test the Data Acquisition (DAQ) system to be integrated into the liquid propellant rocket (LPR) design at Morgan State University. The study involved programming both Arduino and Raspberry Pi to measure the pressure and temperature readings of the propellant tanks and combustion chamber, in order to make a comparison between the two microcontrollers. Arduino boards (UNO and Nano), along with temperature and pressure sensors, were used to build the DAQ system. Arduino codes were written in the sketch files and uploaded to measure the temperature and pressure readings from the MAX6675 and barometric pressure sensor respectively. These collected results from the DAQ system were compared with results from the several temperature and pressure meters under different conditions (e.g., cold water, hot water) for the Arduino-based temperature sensor and air compressor for the pressure transducer. Results indicated that the developed DAQ system is capable of measuring temperature and pressure with minor errors. The results of this study may benefit the ongoing liquid rocket design at Morgan State University with the aim of reaching 13,000 ft altitude.
The Morgan State University, ARROW Rocketry Team, is developing a single-stage liquid-propellant rocket (LPR) with a targeted apogee of 13,000 feet. Due to the complexity of the LPR, each component of the rocket must be studied and investigated thoroughly. The ARROW Rocketry Team has decided to use a Featherweight GPS System to track the position of the liquid propellant rocket. During Morgan State’s previous launching of their solid-propellant rocket, an unexpected error occurred in which the Featherweight GPS recorded incorrect data. One of the leading hypotheses of this error is the location of the tracking device inside the rocket that causes system interference with other devices. A reliable GPS system is needed to accurately record the apogee and location of the liquid propellant rocket. To conduct an experimental analysis of the reliability of the Featherweight GPS system, the MSU Rocketry Team isolated the tracking device and placed it inside the nose cone rather than in the altimeter bay. During the rocket launched on the second day of July 2021, the data collected from the Featherweight GPS system was 98.74% similar to the result of the simulated data. Thus, the MSU Rocketry Team decided to use the Featherweight GPS system on their liquid-propellant rocket. Moreover, a wide variety of research and peer-reviewed journals that deal with the rocket’s nose cone and the characteristics of its airframe are already publicly accessible. However, there are only a few in-depth studies that deal specifically with the rocket’s fin. Thus, this research not only focuses on studying the property of the GPS system, but as well as how different factors, such as the types of fins – clipped delta and trapezoidal; the number of fins – 3 and 4; fin materials – carbon fiber, aluminum, and fiberglass; and its geometric dimensions – root chord, sweep angle, and chord height, affect the rocket’s overall performance. Through the usage of the OpenRocket Simulator, a wide variety of data was collected that shows possible outcomes on both the rocket’s apogee and stability. Additionally, a factorial design – Design of Experiments (DOE), was created using the data collected through the Minitab Statistical software to perform statistical analysis in finding the significant factors and creating both surface and contour plots. Results indicated that the best design to reach the maximum apogee is a three (3) clipped delta-shaped tail fin design made of fiberglass material. The fiberglass material is desirable for a rocket fin because of its chemical and physical properties. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It has a similar strength to materials with much greater densities and much greater strength than most materials of similar density. It is very durable and resistant to most forms of moisture and corrosion.
From mid-May to the end of July, Grace Warznak had an internship with the HelicitySpace Corporation at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County through Maryland Space Grant Consortium. The internship involved writing code and machining parts for the assembly of the first iteration of the Helicity Drive, a fusion space propulsion system using peristaltic magnet compression.
We are modernizing the method of measuring horsepower and efficiency on one of the last two surviving liberty ships. We faced many challenges getting a functioning set up and still have future challenges for the main engine.
A slightly in depth look at the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission and how we plan to aid the confirmation of exoplanet candidates. I will also discuss how to select candidates for follow up observations, calibrating images, and the application of photometry to obtain the desired light curve.
We report on preliminary results of a statistical study of student performance in more than a decade of calculus-based introductory physics courses. Treating average homework and test grades as proxies for student effort and comprehension respectively, we plot comprehension versus effort in an academic version of the astronomical Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (which plots stellar luminosity versus temperature). We study the evolution of this diagram with time, finding that the “academic main sequence” has begun to break down in recent years as student achievement on tests has become decoupled from their homework grades. We present evidence that this breakdown is likely related to the emergence of easily accessible online solutions to most textbook problems, and discuss possible responses and strategies for maintaining and enhancing student learning in the online era.
We will take questions for the final group of presenters and any remaining questions for earlier presenters. Questions may be entered in Zoom chat or online Q&A tool — be sure to specify to which presenter your question is addressed. If time permits additional questions will be taken from the audience — use “Raise Hand” function to be called on by moderators.