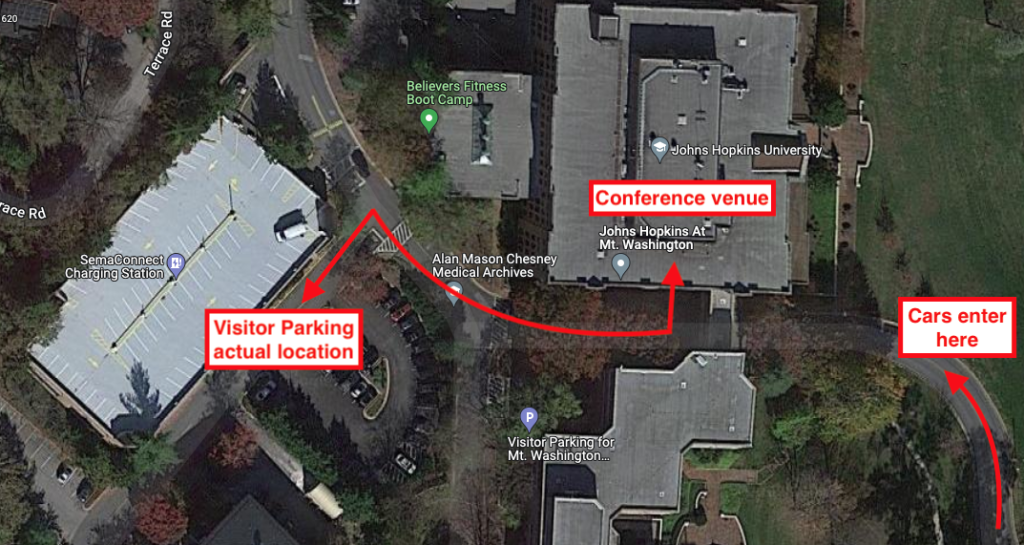
The 2022 MDSGC Student Research Symposium was held in person on Friday, July 29, beginning at 8 a.m. EDT. The venue was the Mt. Washington Conference Center in Baltimore, MD. For GPS navigation, aim for “Johns Hopkins At Mt. Washington, Smith Avenue, Baltimore, MD” (link) and park in the nearby visitor parking lot/garage. Here is an image from Google showing the relative locations of parking and the conference venue:
This year’s symposium showcased presentations by student interns and researchers working at sites across Maryland. The cohort of presenters represent diverse institutions, including: Capitol Technology University, Hagerstown Community College, Johns Hopkins University, Morgan State University, NASA, Towson University, University of Maryland Baltimore County, University of Maryland College Park, and University of Maryland Eastern Shore. We congratulate our students on a successful summer and look forward to seeing more of their work in the future!
The program follows.
2022 MDSGC Student Research Symposium Program
Session 1, 9:00 – 10:30 a.m.
The rocketry team at Morgan State University (MSU) is currently designing a single-stage liquid-propellant rocket (LPR) to achieve an apogee of 50,000 feet. Due to the complexity of an LPR, each component of the rocket will have specifications that must be followed to meet the desired apogee when launched. One critical component of the rocket is the avionics bay since it is responsible for collecting the necessary data, such as the apogee, temperature, pressure, velocity, and ensuing communications with the deployment sensors for easy recovery after launch. Hence, this paper focuses on the avionics bay design of MSU’s LPR and the integration of the DAQ Hat instrumentations. Furthermore, this task entails programming the selected Raspberry Pi 4B model to obtain the readings from the temperature and pressure sensors connected to MCC DAQ Hat devices and logging the data into multiple SD cards for redundancy. Lastly, when the correct code is uploaded and all the connections are correctly done, testing each component individually can proceed to ensure they are operating properly. A high-resolution camera will be connected to the Raspberry Pi flight computer to record the rocket flight, which can be installed into the system. All the subsystems will be integrated into the payload system. Overall, the team achieved both design and integration of the necessary components of the avionics bay of MSU’s LPR.
Sea level rise and land subsidence have been widely recognized as major drivers of geomorphic and ecological change in the Chesapeake Bay area. The Relative Sea Level Rise (RSLR) in the Baltimore Inner Harbor is the combination of absolute sea level rise (ASLR) due to global warming, and land subsidence (LS) due to tectonic downward movement. In this study, two sets of data were analyzed: the NOAA tide gauge in Inner Harbor which has actively monitored the changes in sea level since 1902 for 118 years and the GPS station BACO, 10 miles north of the Inner Harbor tide gauge station, which has recorded land surface elevation change from 2008 to 2019. A piecewise trend of the RSLR is summarized based on the linear trend before 1992 in the twentieth century and the quadratic trend since 1992. The 11-year BACO GPS data indicate a land subsidence rate of 1.90 mm/yr in trend. We estimate a uniform ASLR of 1.1 mm/yr by removing LS rate of 1.90 mm/yr from a RSLR of 3.0 mm/yr during 1902-1992 and its acceleration of 0.1422 mm/yr^2 after 1992. Results suggest that Baltimore should implement more flood prevention plans specifically in Inner Harbor as it is in the coastal area and is heavily affected by the land subsidence issue.
This presentation highlights the experience at the United States Naval Academy. The goal was to create an experiment that would be recreated by K-16 participants as well as assist the STEM team in outreach. The experiment created focused on corrosion prevention. The outreach the STEM department performed included Summer Heroes Youth Program in June and STEM Educator Training in July.
The Centrifugal Mirror Fusion Experiment is a magnetized plasma experiment in a mirror configuration. Using MRI magnets and an ultra high vacuum (UHV) chamber, the experiment will confine high temperature plasma at fusion conditions to produce energy from fusion products. The ultimate goal of the experiment is enabling the commercial availability of compact thermonuclear fusion reactors. The team has designed the Gas Mixing System for the Centrifugal Mirror Fusion Experiment (CMFX) to control the concentration of the helium, hydrogen, and later in the project, deuterium mixture . The system shall deliver the mixture to the HPV chamber. Using a gas puff valve, a mixture with a number density up to n=10^ 19 m^ -3 will dispense into the HPV chamber in 1-1000th millisecond. The Gas Mixing System will operate weeks on end without having to resupply the system with gas as each puff would dispense 0.0002% of the occupying pressure in the system’s volume.
Throughout the internship during the summer of 2022 at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore(UMES), a variety of technologies related to automation and soft robotics were explored. Ongoing efforts reported in recent technical articles published by researchers at several universities and research laboratories were studied. Pick and place tasks using commercially available soft grippers attached to industrial robotic arms installed in the UMES robotics laboratory were implemented. Also, a Raspberry Pi-based small robotic device, popularly known as GoPiGo was programmed to perform simple line following application and pick and place operations using a novel soft gripper put together in the laboratory using 3D printed flexible filaments. Finally, trials were conducted using “ Programmable Air” an Arduino Nano microprocessor-based soft robot controller that can blow and suck the air out of inflatable elastomer shapes cured on 3-D printed molds with appropriately designed pneumatic channels. Soft components were molded using elastomers based on MIT’s Inflatibit soft robots, integrated with IRobot Create 2 ( the base platform for the Roomba vacuuming robot) platform and controlled using a Raspberry Pi and “Programmable Air”. Some refinements will be necessary before the task assigned for the set-up is properly completed. During the internship, opportunities were provided to participate in aerial imaging missions using a drone, programming a 3-axis Cartesian robot (FarmBot) to seed and irrigate on a raised bed and work with other robotic devices such as a robotic boat and ground robot that are under development in the UMES laboratory with a team of students.
Air pollution is a global health concern and has led to millions of premature deaths. In overpopulated cities, pollutants such as CO, NO2, O3, PM2.5, PM10, and SO2 have disastrous effects on human health and exacerbate respiratory illnesses. COVID-19-related lockdowns and restrictions have played a major role in air quality and human health. The cities observed in this study are Kolkata, Milan, Los Angeles, São Paulo, Shanghai, and Sydney. The biggest contributors to air pollution in Los Angeles and Sydney were natural wildfires that increased concentrations of PM2.5. In Kolkata trash burning, diesel engines, and coal combustion led PM2.5 and NO2 to increase during the winter months. Milan’s topography promoted PM2.5 concentrations by casting a thick and protective fog over the area during the winter months. The deforestation of the rainforests in Brazil promoted PM2.5 by causing droughts in São Paulo, which made the city very dusty and worsened the air quality. Shanghai is the most populated city in this study, and rapid socio-economic development, vehicle, and factory emissions, and also a heavy reliance on coal-powered heating lead to heightened Particulate Matter and Ozone levels. By analyzing the effects of the COVID-19 pandemics on air quality, the scope for environmental restoration is seen as people and governments learn what contributes to air quality, and how humans can manipulate it. The findings from this study, and other contemporary ones, could aid in efforts towards combating climate change and sustaining human life.
This project attempts to combine several behaviors seen in nature through animals that form large groups and potentially can show how patterns can develop in any large groups of creatures. Utilizing efforts of past biologists and roboticists, the research conducted with the kilobots hopes to unlock as many secrets of the animal world as possible by studying the behavioral patterns formed in nature and understanding how to replicate and improve upon those processes.
-
-
- Space Junk: The Debris Strikes Back — Madelyn Pollack (UMBC/NASA)
- Thermo-Acoustic Refrigeration — Sean Beahn (TU)
- Mg II Emission from Low Mass Galaxies at Half the Age of the Universe: Implications for Reionization — Ying Qin (JHU)
- Commissioning and Integration of the Asteroid Large aperture PHotometry exoplAnet transit (ALPHA) Observatory — Julianna Reese (UMCP/CTU)
- Magnetic Perpetual Motion? — Daniel Roland (TU)
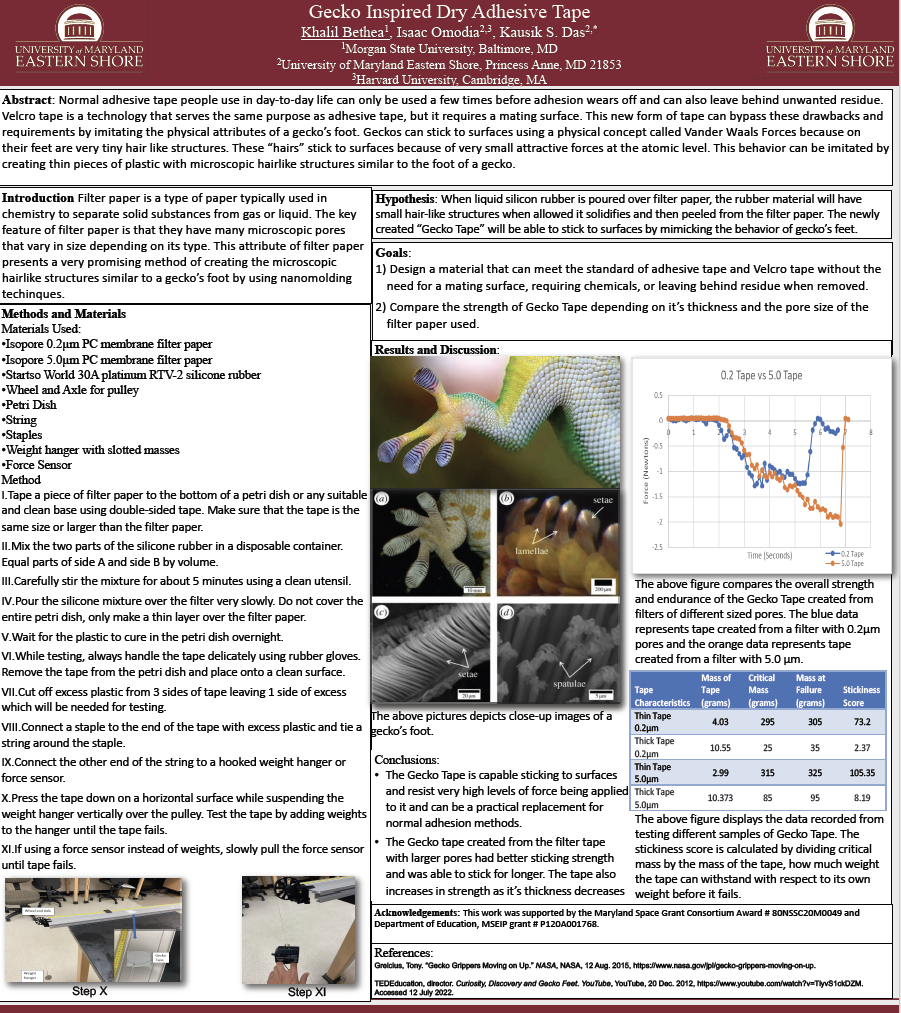
- Gecko Inspired Dry Adhesive Tape — Khalil Bethea (MSU/UMES)
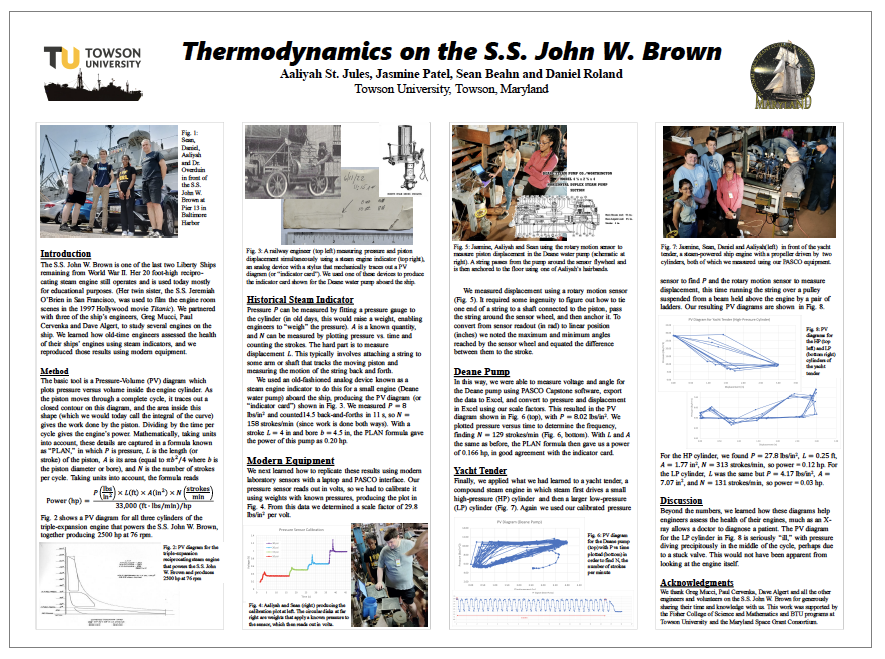
- Thermodynamics Aboard the S.S. John W. Brown — Aaliyah St. Jules (TU)
-
Lunar Rover Wheel Testing — Evan Lewis (CTU/UMCP) & Ali Arnaout (UMBC/UMCP)
-
Group Photos, 10:30-10:45 a.m.
Poster Session, 10:45 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
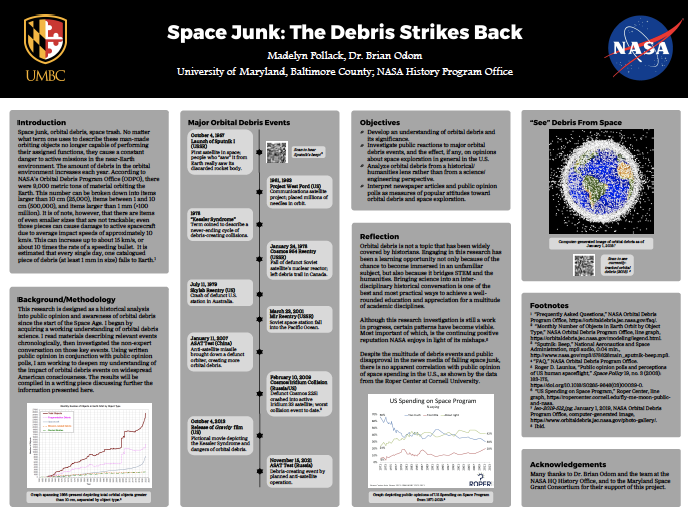
Space Junk: The Debris Strikes Back — Madelyn Pollack (UMBC/NASA)
Space junk, orbital debris, space trash. No matter what term is used to describe these man-made orbiting objects no longer capable of performing their assigned functions, they cause a constant danger to active missions in the near-Earth environment. This presentation will introduce the relationship between orbital debris events and public opinion of spaceflight in the U.S. (Click image for full size.)
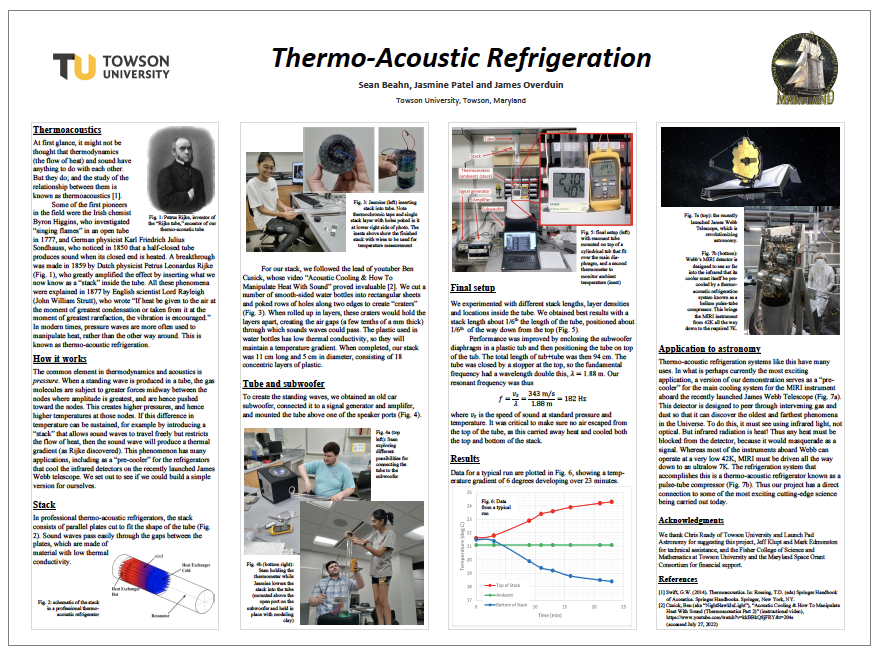
Thermo-Acoustic Refrigeration — Sean Beahn & Jasmine Patel (TU)
We report on the design and construction of a thermos-acoustic tube, in which a standing wave creates higher pressures (and hence temperatures) at the nodes than at the center. A layered plastic “stack” enables sound waves to pass through easily, but impedes the flow of heat. Hence a temperature gradient develops along the stack. We present some preliminary results, and discuss how a more advanced version of this demonstration allows the James Webb telescope to reach the ultra-low temperatures necessary for astronomical observations deep in the infrared band. (Click image for full size.)
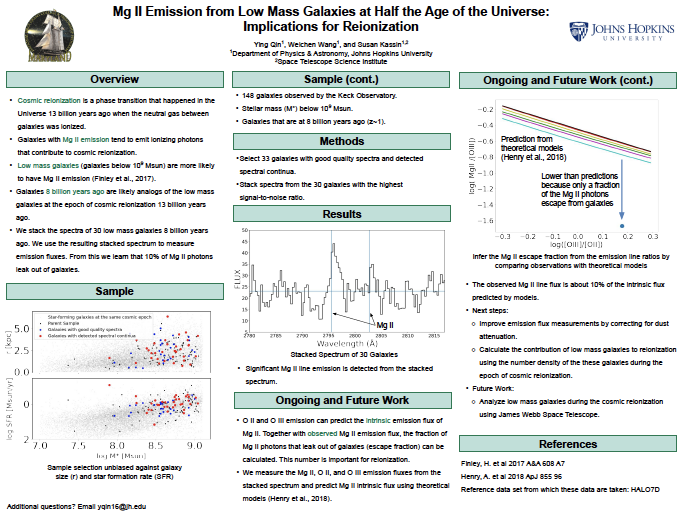
Mg II Emission from Low Mass Galaxies at Half the Age of the Universe: Implications for Reionization — Ying Qin (JHU)
Galaxies today are surrounded by ionized gas, whereas, more than 12 billion years ago, the Universe was filled with neutral gas. This transition from the neutral state to the ionized state is known as cosmic reionization and is believed to be caused by energetic photons which leaked from galaxies. However, galaxies come in a variety of masses, and it remains to be known the masses of the galaxies that reionize the Universe. In this project, we stack 30 galaxies below 10^9 Msun 8 billion years ago and measure the Mg II, O II, and O III emission fluxes from the stacked spectrum. We find the observed Mg II line flux is ~10% of the intrinsic flux predicted by models. This number can be used to calculate the contribution of low mass galaxies to reionization together with the known numbers of these galaxies during the epoch of cosmic reionization. (Click image for full size.)
Commissioning and Integration of the Asteroid Large aperture PHotometry exoplAnet transit (ALPHA) Observatory — Julianna Reese (UMCP/CTU)
The purpose of this project was to commission an observatory at Capitol Technology University (CTU) to track, identify, and perform orbit determinations on near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids and comets. Over the commissioning process, the observatory dome, cameras, and telescope were assembled and configured to move synchronously. The associated software was configured with them to automatically make observations according to designed plans, making the process of collecting data simpler and more accurate than if done manually. Additionally, observations could be monitored and control administered remotely via AnyDesk. Each component was calibrated to ensure proper tracking, alignment, guiding, and focus.
Upon completion of commissioning activities, various observations were made, including 17 unique NEOs. The sensitivity of the system allows objects as faint as 17th magnitude to be detected. Each set of data was processed to account for noise and to identify and track the object(s) captured, then submitted in a report to the Minor Planet Center (MPC). After making several successful reports, the MPC awarded the ALPHA Observatory its own code, W58. (Click image for full size.)

Magnetic Perpetual Motion? — Daniel Roland & Aaliyah St. Jules (TU)
We investigate both theoretically and experimentally the possibility of a magnetic “perpetual motion machine” originally described by the medieval physician Pierre de Maricourt and later popularized by the Jesuit scholar Jean Taisner. A permanent magnet pulls an iron ball up a ramp, only for it to fall through a hole, return to the bottom of the ramp, and repeat. Due to losses by friction and demagnetization, the motion cannot be perpetual. But we investigate whether even a single loop is possible in principle. We derive and experimentally confirm an empirical force law and use this to obtain intriguing preliminary results. (Click image for full size.)

Gecko Inspired Dry Adhesive Tape — Khalil Bethea (MSU/UMES)
Normal adhesive tape people use in day-to-day life can only be used a few times before adhesion wears off and can also leave behind unwanted residue. Velcro tape is a technology that serves the same purpose as adhesive tape, but it requires a mating surface. This new form of tape can bypass these drawbacks and requirements by imitating the physical attributes of a gecko’s foot. Geckos can stick to surfaces using a physical concept called Van der Waals Forces because on their feet are very tiny hair-like structures. These “hairs” stick to surfaces because of very small attractive forces at the atomic level. This behavior can be imitated by creating thin pieces of plastic with microscopic hairlike structures similar to the foot of a gecko. (Click image for full size.)
Thermodynamics Aboard the S.S. John W. Brown — Aaliyah St. Jules, Jasmine Patel, Sean Beahn, & Daniel Roland (TU)
We explore the uses of steam engine indicators to characterize the performance of different engines aboard the Liberty Ship S.S. John W. Brown, one of the only two reciprocating-engine steamships still surviving from World War II. We first use a historical indicator (a steam-driven analog device) to reproduce a pressure-volume diagram for a small water pump. We then replicate this diagram using modern laboratory equipment and a PASCO interface. Finally, we repeat this for both cylinders of a small marine steam engine. In all cases we use our diagram to calculate engine power, and to diagnose its overall “health”. (Click image for full size.)
Lunar Rover Wheel Testing — Evan Lewis (CTU/UMCP) & Ali Arnaout (UMBC/UMCP)
The goal was to design a testing apparatus capable of testing the wheel that will be used by a lunar rover project, collecting data such as soil (lunar regolith) pressure created by the wheel, rolling resistance of the wheel, and soil displacement created by the wheel. (Click image for full size.)

Vibration-Induced Elasto-hydro-dynamic Adhesion of Thin Elastic Sheet — Isaac Omodia (UMES/Harvard), Kausik S. Das (UMES), & L. Mahadevan (Harvard)
When a thin elastic sheet is vibrated close to a wall, it leads to an adhesive effect first described by Weston-Dawkes et al. Here we quantify and describe the adhesive force as a function of the vibration frequency, vibration amplitude and the size of the elastic sheet. We show that the adhesion force increases with increasing frequency, amplitude and radius of the thin elastic sheet. (Click image for full size.)

Lunch, 12:00 – 12:55 p.m.
Session 2, 12:55 – 2:00 p.m.
The expansion of space innovation and exploration is possible through diverse partnerships and with the support of the Office of International and Interagency Relations (OIIR) at NASA. This summer a graduate student from rural North Carolina had the opportunity to witness diplomacy in action and apply classroom lessons to meaningful work. Follow her journey as she dives into a new field of interest and confirms her commitment to public service.
This presentation will describe the experiences had by an MDSGC intern at the United States Naval Academy. Over the course of the summer, the interns helped with the USNA STEM center’s outreach programs, including SeaPerch, SET (Stem Education Training) Sail, and SHYP (Summer Heroes Youth Program). Michael focused his project on creating an educational bridge building kit while going through the engineering design process.
Two important elements for a liquid rocket are the nose cone and propellant tanks. One purpose of this project is to analyze the nose cone shape, length, and material selections. OpenRocket simulation and MiniTab analysis are used to seek a relationship between the nose cone factors and the altitude reached in flight. The analyzed data shows which factors have a significant impact on the altitude, providing a statistics-based recommendation among the shape, length, and material. The collected and examined data only offers insight into the critical factor; it does not suggest a particular shape, length, or material. The second purpose of this work is the 3D model progression of the propellant tanks created using OnShape computer-aided design. Overall, the results of this project will be used for Morgan State University’s Liquid Propellant Rocket (LPR).
During the internship in the summer of 2022 at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore(UMES), a variety of robotics and automation technologies including soft robotics were explored. Ongoing efforts reported in the latest technical articles published by researchers at several universities and research laboratories were studied. Recent articles published by the AIRSPACES project team were also studied. Pick and place tasks using commercially available soft grippers attached to industrial robotic arms installed in the UMES robotics laboratory were implemented. Simple flexible automation tasks were also implemented using the six-degree of freedom industrial robot and a four-degree of freedom SCARA robot equipped with a vision system in the laboratory. Preliminary trials were also conducted with “ Programmable Air” an Arduino Nano microprocessor-based soft robot controller that can inflate and deflate elastomer shapes cured on 3-D printed molds with appropriately designed pneumatic channels. During the internship opportunities were provided to participate in aerial imaging missions using a drone, programming a 3-axis Cartesian robot (FarmBot) to seed and irrigate on a raised bed and work with other robotic devices such as a robotic boat and ground robot that are under development in the UMES laboratory with a team of students. Significant effort was devoted to attaching, calibrating, and programming several water quality sensors on a robotic boat and conducting field trials with the set-up in a UMES pond. Valuable experience was gained in working with the Arduino microprocessor board to record the geo-located sensor data and navigating the boat autonomously using PIXHAWK open source autopilot.
I use a modified Turtlebot3 robot to draw pictures using Bézier curves. I briefly describe our robot’s physical design. I discuss my program which converts images to paths using Bézier curves. I use a carrot tracking algorithm with a PID controller to follow the paths produced. I present the robot’s drawings and discuss the results.
The history of physics is a history of discoveries, which are not properly understood at the time of discovery! Deeper understanding develops over decades: with the happy result that fundamental physics is, today, almost entirely simple, easily understandable, high-school algebra.
