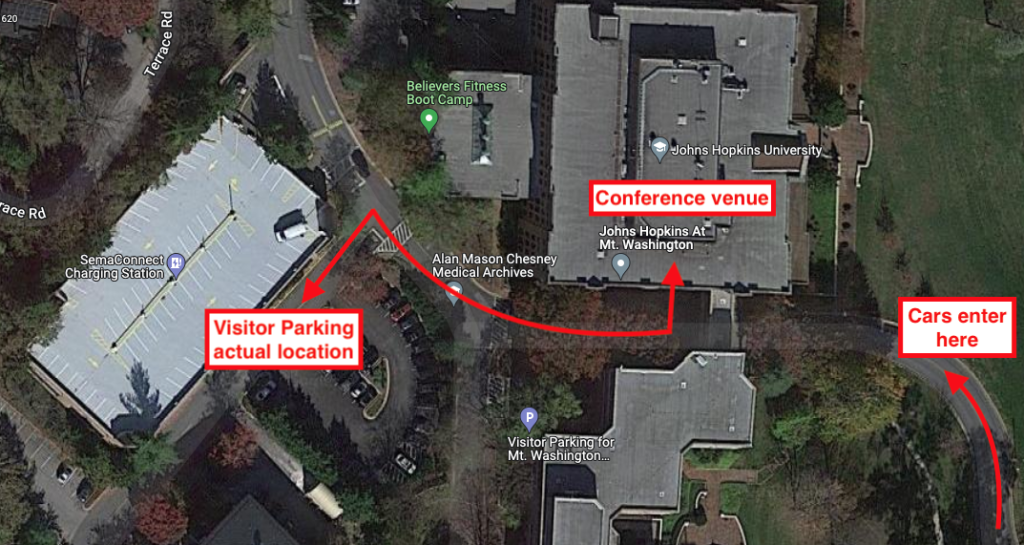
The 2023 MDSGC Student Research Symposium was held on Monday, July 31, beginning at 8 a.m. EDT. The venue was the Mt. Washington Conference Center in Baltimore, MD. For GPS navigation, aim for “Johns Hopkins At Mt. Washington, Smith Avenue, Baltimore, MD” (link) and park in the nearby visitor parking lot/garage. Here is an image from Google showing the relative locations of parking and the conference venue:
This year’s symposium showcased presentations by student interns and researchers working at sites across Maryland. The cohort of presenters represent diverse institutions, including: Capitol Technology University, Hagerstown Community College, Johns Hopkins University, Morgan State University, NASA, Towson University, University of Maryland Baltimore County, University of Maryland College Park, and University of Maryland Eastern Shore. We congratulate our students on a successful summer and look forward to seeing more of their work in the future!
The program follows.
2023 MDSGC Student Research Symposium Program
Session 1, 9:00 – 10:50 a.m.
The focus of this project lies on developing a satellite simulation to train spaceflight operation students attending Capitol Tech University, closely emulating real-life scenarios. The simulation replicates a segment of satellite EO-1, where solar array wings are controlled by the SA Drive and SA Deployment. Operating as an interconnected network, the system comprises multiple languages in Galaxy. Initiating one command sets off a cascade of interrelated procedures, utilizing database mnemonics to establish a continuous information exchange loop that is systematically updated on the display page. Throughout orbital cycles, testing involves tackling challenges related to debugging and error configuration. The simulation’s success grants invaluable hands-on experience in satellite operations, significantly advancing our comprehension of solar array behavior and energy management in space.
Mobile robotics is used in a variety of applications in our present age. NASA uses mobile robots for space science and earth science related observations and data collection. I worked on using two mobile robotic platforms during my summer internship at University of Maryland Eastern Shore (UMES), Sphero RVR and Sphero BOLT, and learned to program them using Scratch and Python to follow predefined trajectories while collecting data from sensors that are integrated with the robots. I also installed a soft gripper which was activated using an Arduino Nano-based Programmable Air module on the RVR. Effective communication was established between the RVR and the Programmable Air module to carry out simple pick and place operations. I also programmed the BOLT to follow the Sphero RVR as it moved on a circular trajectory using a infrared red signal.
During the internship at the US Naval Academy, while participating as a teaching assistant in the “SHYP” (Summer Heroes Youth program) and “Set Sail” programs, the concepts learned from creating a sea perch for marine engine propulsion, with the inspiration of the amphibious helicopter and the sea plane were applied. The project consists of two parts: a device for floating, and a part for flying. The two small prototypes were made with playful materials that could be found at home and/or bought online. For the circuitry, the Arduino Uno was connected to the servo motors, which were programmed using Python, and rotate the propellers for thrust. The sea perch kit used to build the floating device has three motors, a preprogrammed controller, a 12-volt battery, a tether for connecting the controller to the motors, and a charger. Overall, even though the teaching programs kept me busy, I had a fun time experimenting with simple materials and getting hands-on experience with propellers and motors.
“Get a summer job”, his parents told him. This left me looking for a wide variety of ways to spend my summer. Little did I know this wouldn’t be a summer to forget. Not long after searching for a job to occupy my time, I found two amazing programs offered by the Maryland Space Grant Consortium. This was my golden ticket to an eventful summer that had a deeper meaning to me and my career goals. This led me to be working in two separate summer programs, I had the opportunity to introduce middle schoolers to STEM projects and create a data retrieving unit for a sounding rocket payload.
During my time at Morgan State University I worked on assembling the avionics system and testing various components like my thermocouples, pressure transducer, and pi-camera. I tested the thermocouples by using hot and cold water and I also tested my pressure transducers by pushing air through it using a compressor. I used python to give me readings from the different tests I ran on each component.
Miniature robots apparently still have their uses even in this day and age. These days whenever you think of an autonomous robotic helper we expect them to be somewhat large in size and capable of doing a lot of tasks simultaneously. Though like every great innovation starting in the minor leagues can lead a major impact. Kilobots for example are one of those miniature robots. They have their limits but the experience of experimentation can lead to grand developments.
The project with the Roman Space Telescope’s Deployable Aperture Cover focused on bonded tabs to a non flight collar boom using Non Destructive Inspection.
Analyses of XRD spectra are standard in materials characterization and help resolve structural and phase information. We aim to create a workflow that models XRD spectra in the open-source aflow++ framework and generate a publicly accessible bank of XRD data to enable rapid identification of material compounds.
A passive brain-computer interface (BCI) is a system which collects brain dynamics to assess the mental workload of an individual while they are performing a task. Such systems can be used to support human health, safety, and cognitive-motor performance while conducting long-term space habitation in future Artemis missions. However, passive BCI requires an accurate method for the classification of mental workload using a short duration segment of brain activity. Therefore, we seek to develop a computational model for the offline classification of three different states of workload. An electroencephalography (EEG) device is used to assess the mental workload of participants completing a complex action sequence to solve a puzzle with a teammate. The collected EEG data was preprocessed and segmented into 10-second components. Features were extracted by transforming the EEG signal into a complex network by means of the visibility graph (VG) algorithm. Then, the VGs of multiple EEG channels were assembled into a multiplex temporal network (MTN). The structural properties of the MTNs were measured and fed to six different supervised-learning classifiers. Additional features were also computed with the spectral power of six frequency ranges. Classification of mental workload was performed individually for each subject’s data. Results show that a support vector machine classifier achieved a 98% mean testing accuracy when tasked with the prediction of mental workload using 10 seconds of EEG data. All other classifiers studied achieved at least a 92% mean testing accuracy in classification. The results suggest that the computational model presented here has the potential to enable the use of pBCI technology in future Artemis missions.
-
-
- Baryonic Tully Fisher Relation for Galaxies with Supernova Distances — Shannon Markward, Aaron Torster (Towson)
- ALPHA Observatory Campaign 7 Data Analysis — Meredith Embrey (UMCP/CTU)
- Preliminary Trials With GoPiGo3 and LIMO Robots in Virtual and Physical Realm — Andrew Duck, Urjit Chakraborty, Lucas Marschoun (UMES)
-
Group Photos, 10:50-11:10 a.m.
Poster Session, 11:10 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
Baryonic Tully Fisher Relation for Galaxies with Supernova Distances — Shannon Markward, Aaron Torster (Towson University)
The Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation (BTFR) is an empirical correlation between the baryonic mass of a spiral galaxy and its rotational velocity. As the equation for baryonic mass is dependent on the luminosity of a galaxy, it is also true to state that it is an empirical correlation between distance and the mass of the galaxy. By using the BTFR, we avoid using so-called “standard candles,” such as Type Ia supernovae or Cepheid variable stars, which are limited to use in relatively nearby galaxies. The BTFR provides an alternate approach for measuring distance that is then applicable to a much larger sample. We present an update on the data collection and analysis pipeline for an ongoing project of the Undergraduate ALFALFA Team (UAT), for which the primary science objective is to generate a well-defined BTFR. We used the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) to observe and measure the HI 21-cm emission line profiles of 200 galaxies in our observing sample with accurately known distances from the Democratic Samples of Supernovae (Stahl et al. 2021). Here, we will focus on the observing sample and show: (1) progress to date on obtaining the HI 21-cm measurements; (2) preliminary outcomes of our newly developed analysis tools; and (3) statistical analysis of sample signal-to-noise, including non-detections. (Click image for full size.)
ALPHA Observatory Campaign 7 Data Analysis — Meredith Embrey (UMCP/CTU)
The ALPHA Observatory Campaign 7 analyzed 1 Terabyte of data from ALPHA’s first run not just focused on asteroids but also variable stars and exoplanets. The images of all objects are run through multiple scripts to determine the eligibility to be submitted. Asteroids are checked for quality and accuracy, while exoplanet and variable star data are also graphed into a light curve to determine the transit period. This is ALPHA’s first run observing exoplanets, and even observed a pending exoplanet. (Click image for full size.)
Preliminary Trials with GoPiGo3 and LIMO Robots in Virtual and Physical Realm — Andrew Duck (UMBC/UMES), Urjit Chakraborty (UMES), Lucas Marschoun (UMES)
This poster outlines the summer project work carried out by student volunteers and a UMES undergraduate related to the LIMO, GoPiGo3 and Moorebot Scout, mobile robotic platforms, in both online virtual environments and the real world. The preliminary efforts were devoted to line following applications using PID controls on the GoPiGo3 and basic AI integration in coordination with the Moorebot Scout. The project team also explored the use of Lidar technology and programming in python with both the GoPiGo3 and the LIMO robots. (Click image for full size.)

Lunch, 12:00 – 1:00 p.m.
Session 2, 1:00 – 2:00 p.m.
This summer at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore under the guidance of my mentors, I explored how agriculture and technology can be integrated to optimize the cultivation of food and collect data. Inspired by developments in research on the viability of different environments in space for growing food, we designed an experiment to test the viability of growing microgreens and kale on the surface of the moon using a simulant of lunar regolith, and we used sensors equipped to a Raspberry Pi microcontroller to measure data about the different treatments we set up. I also explored programming a 3-axis Cartesian robot (FarmBot) to seed, photograph, and irrigate on a raised bed of peanut plants using both manually written code and primitive AI coding capabilities introduced recently in the software. I also got exposed to working with an autonomous ground robot equipped with a Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium (NPK) sensor that is under development in the UMES laboratory with a team of students. I assisted the graduate student in the lab on getting the NPK sensor calibrated properly and logging the data at respective waypoints of an autonomous mission map.
The Centrifugal Mirror Fusion Experiment (CMFX) aims to harness the potential of azimuthal rotation to enhance plasma confinement within a magnetic mirror. The rotation is imposed by applying a high voltage from a capacitor bank to a central electrode, creating a radial electric field that helps stabilize and heat the plasma. Understanding the interactions between the plasma, the capacitor bank, and other external circuit elements is challenging. This work simulates the created plasma as a capacitor in parallel with a resistor. However, the values of these elements were not immediately known. The entire electrical circuit was entered into the LTspice simulation software to find these values. The parameter values of the circuit elements were varied systematically until the simulated plasma current and voltage, measured in the experiment, were qualitatively and quantitatively similar. The results are being compared with theoretical predictions of plasma capacitance and resistance. They are an essential tool for the design of a scaled centrifugal mirror as a fusion energy reactor. Details of the circuit, simulations, and methodology are presented.
This work is supported by ARPA-E Grant No. DE-AR0001270, and by NASA Grant No. 80NSSC20M0049 as part of the Maryland Space Grant Consortium program.
Abstract TBA.
This project investigates how land use influences water quality in the urban environment—specifically, Herring Run. I examined data for the watershed spanning 28 years, looking for patterns and change over time. I based my analysis on water quality observations recorded by the U.S. Geological Survey and the Maryland Department of the Environment. For context, I also included precipitation data from the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. Following methods published by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, I analyzed satellite imagery in Q-GIS™, which I downloaded from the Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics Consortium. To gain field experience, I collected water quality observations from multiple locations along Herring Run on two separate visits, using a HANNAH™ portable meter. Finally, I drafted a report and created a presentation summarizing my research.
The presentation will describe the process of nose design for the rocket, going over best nose cone shapes and a quick demonstration of early 2D CFD (computational fluid dynamics) software results on an early nose cone design. There will be a brief overview of my time at NASA RockOn. It will then go over the design and partial completion of the propulsion tanks for the rocket, with a final look of how a virtual reality headset was used to view the nearly final design in VR.
